There are many instructions for setting up and commissioning IT services. However, the associated instructions for decommissioning are usually forgotten.
The following describes how to correctly decommission a certification authority (Enterprise Certification Authority) integrated into Active Directory.
Questions
Before uninstalling the certificate authority, the following questions should be answered:
- Is the certification authority being decommissioned, or is it to be migrated to another server and continue to operate there? Then see article "Migration of an Active Directory integrated certification authority (Enterprise Certification Authority) to another server„.
- Has the most recent certification authority certificate already expired, or is it still valid? Are there any time-valid certificates still issued by the certification authority?
- Should the server (or its operating system installation) on which the certificate authority is installed be reused for another purpose?
Procedure
Do you know TameMyCerts? TameMyCerts is an add-on for the Microsoft certification authority (Active Directory Certificate Services). It extends the function of the certification authority and enables the Application of regulationsto realize the secure automation of certificate issuance. TameMyCerts is unique in the Microsoft ecosystem and is available under a free license. It can downloaded via GitHub and can be used free of charge.
The process consists of the following sub-steps:
- Timely discontinuation of certificate issuance and rejection of outstanding certificate requests.
- Revocation of all certificates issued that are still valid
- Adjust blacklist validity and issue last blacklist
- Create backup
- Identify private keys
- Uninstalling the Certification Authority Role
- Deleting the certification authority database
- Revocation of the certification authority certificate
- Removing the remaining certificate authority (CA) components from Active Directory
- Deleting the computer account from Active Directory
When parts of the hierarchy are no longer available
Assuming the certification authority has not been in operation for a long time or the root certification authority revocation list has already expired, the certification authority service may not be able to be started.
In this case see article "The certification authority service does not start and throws the error message "The revocation function was unable to check revocation because the revocation server was offline. 0x80092013 (-2146885613 CRYPT_E_REVOCATION_OFFLINE)".„.
Details: Timely discontinuation of certificate issuance and rejection of outstanding certificate requests.
In order to expire all certificates issued by a certification authority on a certain date, the TameMyCerts Policy Module for Microsoft Certification Authority can be used.
This step is only required if the certification authority certificate has not yet expired.
Published certificate templates should be removed by the certification authority so that new certificate requests are not made and certificates issued.
Pending certificate requests should be rejected. Autoenrollment Clients will evaluate this information and clean up the local certificate stores for pending certificate requests accordingly.
Clients should be allowed a certain amount of time to pick up the information and apply it appropriately (depends on how long it is planned to allow clients to be offline).
Details: Revocation of all certificates issued that are still valid
This step is only required if the certification authority certificate has not yet expired. All certificates that are still valid should be revoked in this case.
If the certification authority certificate has already expired, all issued certificates have expired as well, so there is nothing to revoke.
Details: Adjust blacklist validity and issue last blacklist
This step is only required,
- if the certification authority certificate has not yet expired.
- the associated certification authority hierarchy remains in operation, i.e. the root certification authority continues to be trusted.
The revocation list validity should be configured to exceed the expiration date of the certification authority certificate. A new revocation list is then issued. This is held in the revocation list distribution points until the expiration date of the certification authority.
Details: Create backup
In order to be able to restore the certification authority in case of doubt, a last complete backup should be made. private key material included can be created. See the following articles:
- Create a backup of a certification authority
- Create a backup of the private key of a certification authority
If a hardware security module (HSM) is used, the private keys must be secured via its specific mechanisms.
Details: Identify private keys
The uninstall routine does not delete the private keys of the certification authority. We therefore intend to delete them from the system ourselves later. However, the certificate authority certificate is deleted by the uninstall routine, so it makes sense to collect the necessary information in advance.
If a hardware security module (HSM) is used, the private keys must be deleted via its specific mechanisms.
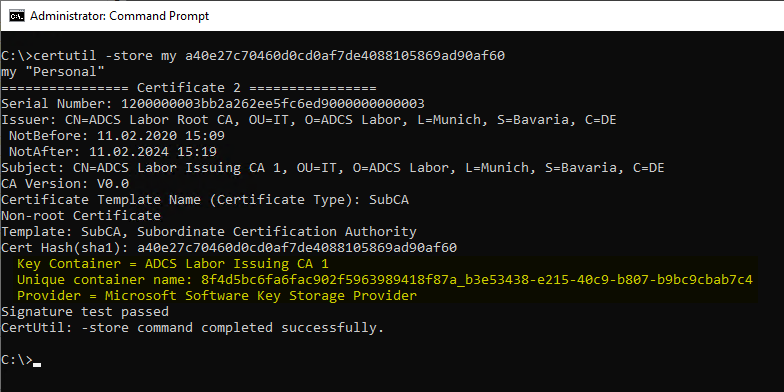
For each certificate authority certificate, its fingerprint (thumbprint, the SHA-1 hash of the certificate) is determined and the necessary information is output with the following command.
certutil -store my {Thumbprint}
The following information is important here:
- Key Container
- Unique container name
- Provider
Details: Uninstalling the Certification Authority Role
An account with Enterprise Administrator privileges is required to uninstall the Certification Authority role. Also, the account must be a local administrator on the certification authority server.
It is enough if the account has the right to delete the pKIEnrollmentService object of the certification authority. Nothing more is done in AD.
Please make sure that the Server Manager is working properly. See also article "Installation or uninstallation of a Windows feature fails with error message "The service is configured to not accept any remote shell requests."„.
Uninstalling the Certification Authority role has the following effects, among others.
- The certification authority certificate is deleted from the local certificate store, but the private key is not deleted.
- The "AIA" object in the Active Directory remains and must be deleted manually if necessary.
- The Enrollment Services object in Active Directory is deleted, thus the bindings of the certificate templates to this certification authority are also invalid.
- revocation list distribution points in Active Directory are retained and must be manually deleted if required.
- The certificate authority certificate is not deleted from NTAuthCertificates, it must be removed manually if necessary.
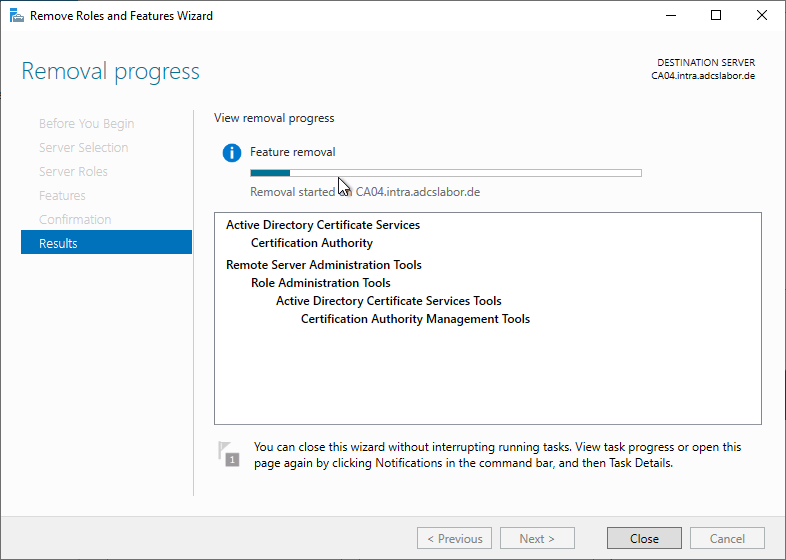
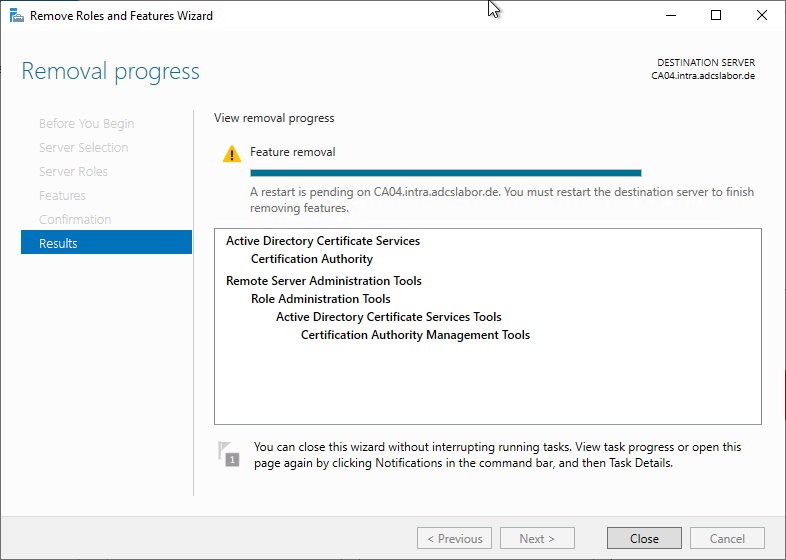
Windows PowerShell can be used to uninstall the Certification Authority role using the following command.
Remove-WindowsFeature ADCS-Cert-Authority
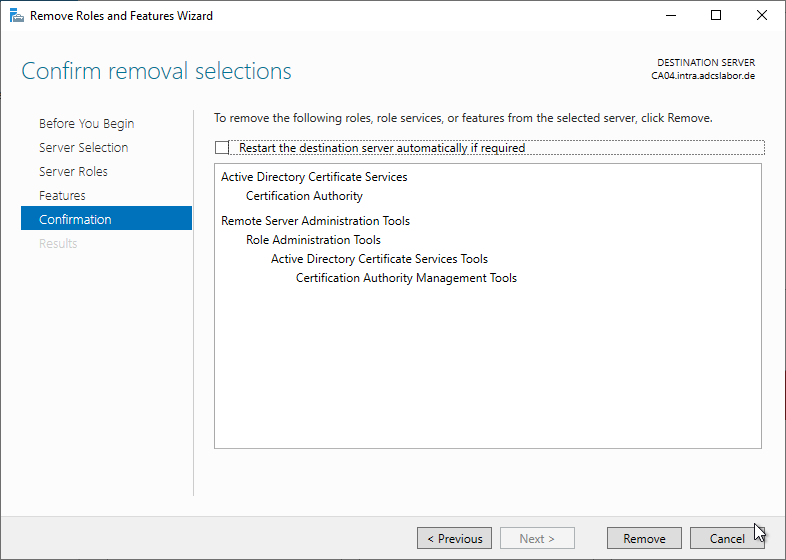
Uninstalling the Certification Authority role is also possible via the Server Manager.
To do this, the "Remove Roles and Features Wizard" is called.
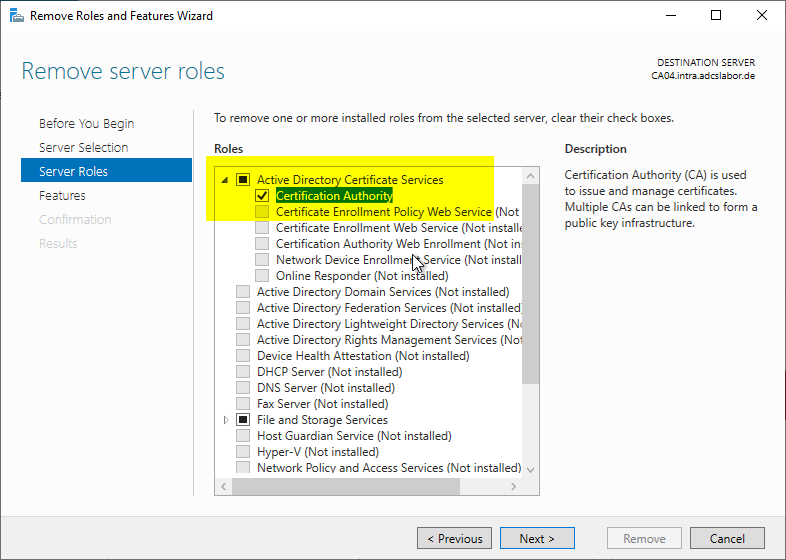
The Certification Authority role is now deselected.
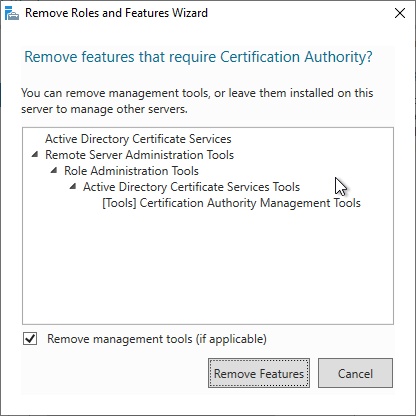
The management tools can be uninstalled. However, if it is the last certificate authority server on the network, it may be helpful to leave them installed for subsequent cleanup.
Details: Delete private key
The procedure that applies to software keys is discussed below. If a hardware security module (HSM) is used, the keys must be deleted via its management tools.
Without the "-csp" parameter, the "-key" command displays only keys that are stored on a Cryptographic Service Provider (CSP) thus for certification authority keys usually none.
certutil -key -csp "Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider
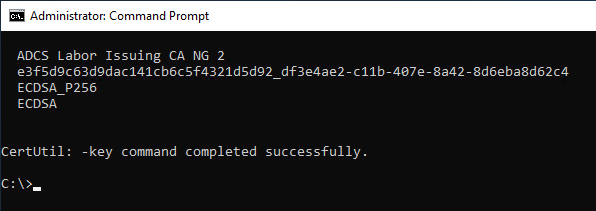
certutil -csp "Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider" -delkey "ADCS Labor Issuing CA NG 2"
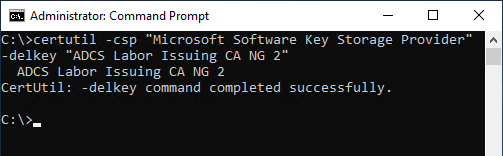
Deletion can also be performed using the displayed key identifier:
certutil -csp "Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider" -delkey {identifier}
Details: Delete the certification authority database
The certification authority database is not deleted by uninstalling the certification authority role. Therefore, it must be deleted manually if you want to continue using the server. The default installation path is located at:
C:\Windows\System32\CertLog
Details: Revocation of the certification authority certificate
The certification authority certificate should now be revoked or the revocation should be ordered from the parent certification authority. See also article "Revoking an issued certificate„.
Details: Removing the remaining Certificate Authority (CA) components from Active Directory.
The following entries in the Public Key Services container in Active Directory are not removed by the uninstallation:
- NTAuthCertificates
- Authority Information Access (AIA)
- CRL Distribution Point (CDP)
Details: Deleting the computer account from Active Directory
If the computer on which the certificate authority was installed is not to be used any further, the computer account can now be deleted from the Active Directory.
Related links:
- Installation or uninstallation of a Windows feature fails with error message "The service is configured to not accept any remote shell requests."
- Migration of an Active Directory integrated certification authority (Enterprise Certification Authority) to another server