Like any software Microsoft Active Directory Certificate Services are also subject to certain limitsimposed by their design.
What is not so obvious is the question of how many Subject Alternative Name (SAN) can be issued with the Microsoft certification authority.
The IETF RFC 5280 describes the structure for Subject Alternative Names as follows:
SubjectAltName ::= GeneralNames
GeneralNames are defined here as:
GeneralNames ::= SEQUENCE SIZE (1..MAX) OF GeneralName
Finally, Appendix B., "ASN.1 Notes" contains the definition for a SEQUENCE of the size "(1..MAX)":
The SIZE (1..MAX) construct constrains the sequence to have at least one entry.
MAX indicates that the upper bound is unspecified.
Implementations are free to choose an upper bound that suits their environment.
According to RFC 5280, there is therefore no limit to the number of Subject Alternative Names in the corresponding certificate extension, which theoretically allows an infinite number of SANs. But what about the Microsoft certification authority?
To find this out, let's write ourselves a little test with the PSCertificateEnrollment PowerShell module, which repeatedly requests certificates and gradually increases the number of alternative requestor names.
Import-Module PSCertificateEnrollment
1..1000 | ForEach-Object -Process {
$sans = @(1..$_ | % { "san-test-$_.intra.adcslabor.de" })
New-CertificateRequest -Subject "CN=A Test" -Dns $sans | Get-IssuedCertificate -ConfigString "CA02.intra.adcslabor.de\ADCS Labor Issuing CA 1" -CertificateTemplate "ADCSLaborWebServer"
}
This goes well for a while, but suddenly the certificate requests are rejected.
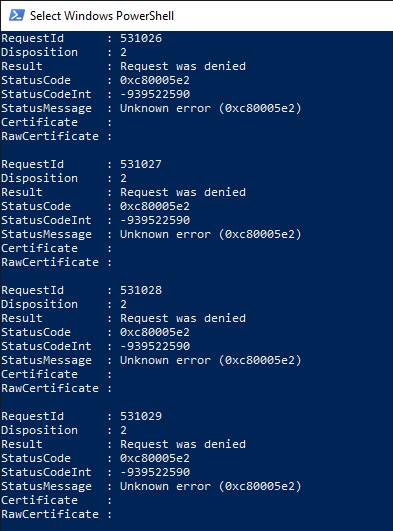
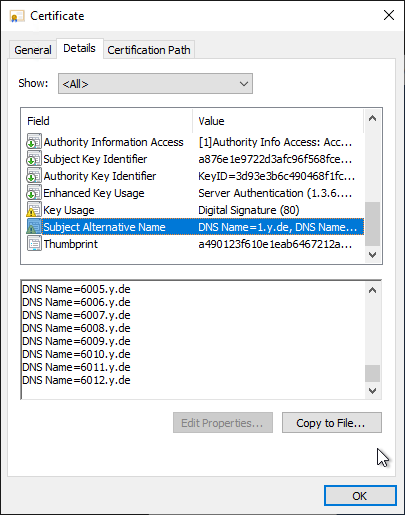
The last successfully issued certificate in our test contains 127 alternative applicant names.
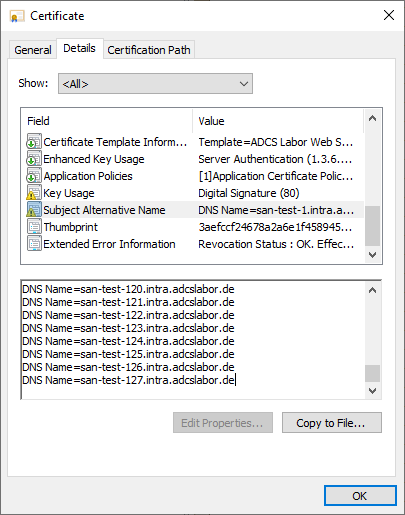
The certification authority reports that a field size has been exceeded for all further certificate requests with more alternative applicant names.
Field length is greater than maximum 0xc80005e2 (ESE: -1506 JET_errColumnTooBig)
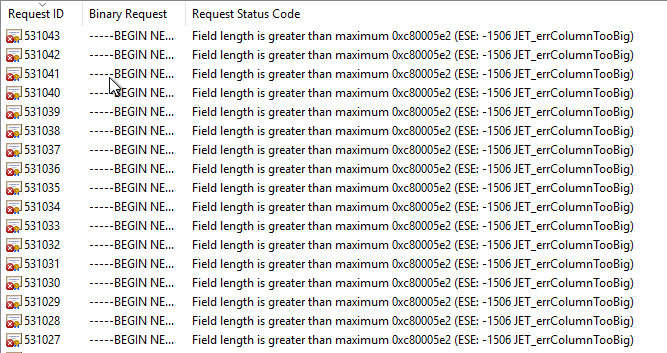
In the event display we find the Event with ID 22 of the source Microsoft-Windows-CertificationAuthority with the same content.
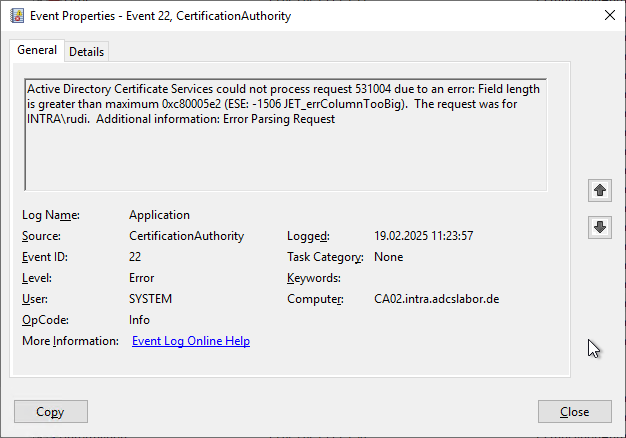
As it turns out, the certification authority is not able to create a database row for the certificate request because the field size has been exceeded.
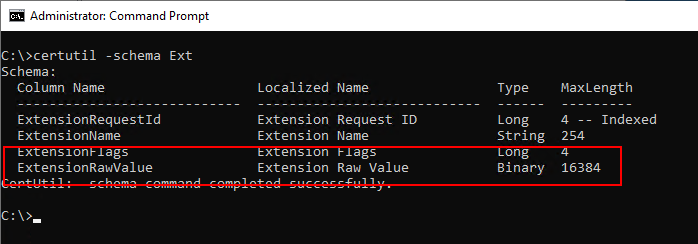
The certificate extensions are stored in a separate field in the certification authority database. As it turns out, this field is limited to 4096 bytes, which is exceeded with additional SANs.
certutil -schema Ext
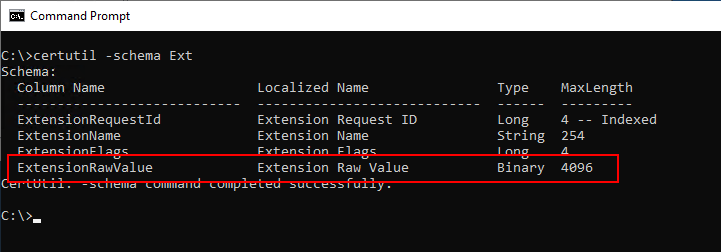
So we have formulated our question incorrectly: There is no restriction on the Quantity of the alternative applicant names, but for the Total size of all certificate extensionsof which Subject Alternative Names is one of many others.
The fact that exactly 127 SANs were possible in my test - a number that suggests other keys in the IT world - was more or less a coincidence. The actual achievable number depends on the number of characters and other certificate extensions in the certificate request, as a new test with significantly fewer characters shows...
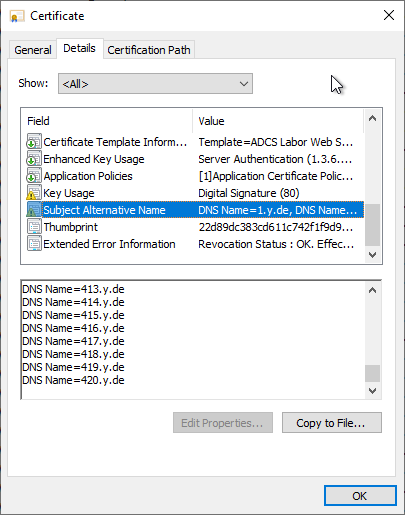
Then I simply do not save the certificate requests in the database
I received a suggestion from a reader that there is the option of not saving the certificate requests in the certification authority database.
This option is of course not useful in most cases, as the corresponding certificates cannot be traced and cannot be revoked.
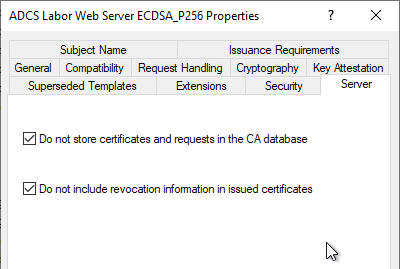
For this option to work, the following global setting must be activated:
certutil –setreg DBFlags +DBFLAGS_ENABLEVOLATILEREQUESTS
Now significantly more SANs and larger certificate extensions are possible before we finally reach the limitations of the MS-WCCE protocol is running.
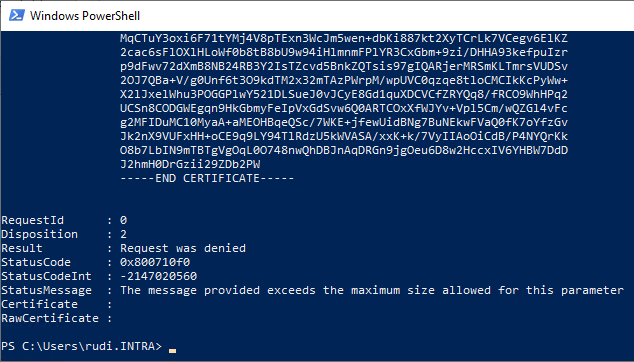
The last successfully issued certificate is approx. 90 kilobytes in size.
Notes
I am curious to see whether the limitations of the certification authority database also apply to statements on the expected support for post-quantum cryptography in the future with the Microsoft certification authority were taken into account, as significantly larger certificates can be assumed here.
Update: Field size can be increased
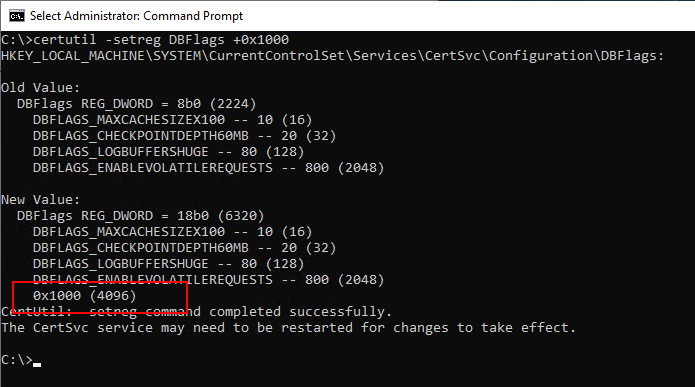
Hans-Joachim Knobloch has pointed out to me that Microsoft has in the meantime has published an articlewhich describes how the database field can be enlarged to 16384 bytes. This new option is also in a YouTube video described.
This option came for Windows Server operating systems from Windows Server 2019 with a patch in 2022:
- Windows Server 2019 - July 21, 2022-KB5015880 (OS Build 17763.3232) Preview
- Windows Server 20H2 - July 26, 2022-KB5015878 (OS Builds 19042.1865, 19043.1865, and 19044.1865) Preview
- Windows Server 2022 - July 19, 2022-KB5015879 (OS Build 20348.859) Preview
certutil -setreg DBFlags +0x1000
As Microsoft mentions in the article, it is no longer possible to restore older backups to the certification authority after changing the database schema. The setting cannot be reversed.
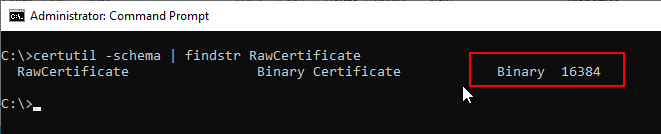
After restarting the certification authority service, we now see that the maximum field size is now 16384 KB.
A new test clarifies whether we can now accommodate four times the number of SANs as expected.
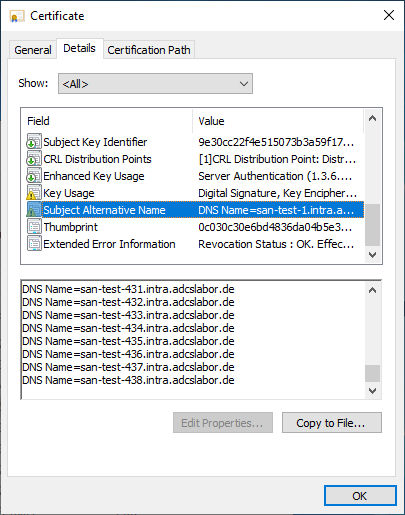
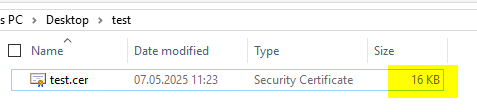
But if we pay close attention, we can see that 438 is not four times the amount of 127. We are now exceeding the limit of another database field - the total size of the certificate is also limited to 16384KB.
certutil -schema | findstr RawCertificate
A simple export of the last successfully issued certificate confirms our thesis.
Related links:
- The database schema of the Certification Authority database
- Details of the event with ID 22 of the source Microsoft-Windows-CertificationAuthority
- Limits of Microsoft Active Directory Certificate Services
External sources
- Don't Believe the FUD - Microsoft PKI is Your Key to Crypto Agility (PKI Solutions LLC)
- How to Set Up a CA for Non-Persistent Certificate Processing (Microsoft)
- Field Report - Mitigating PKI Template Risks for Ephemeral Workloads and Desktop (PKI Solutions LLC)
- How to expand the maximum extension size limit at AD CS (Microsoft)
- Active Directory Certificate Services enhancements, innovations, and security (ITOpsTalk on YouTube)